Monitoring of Riverine Litter
Options and recommendations for the monitoring of riverine litter
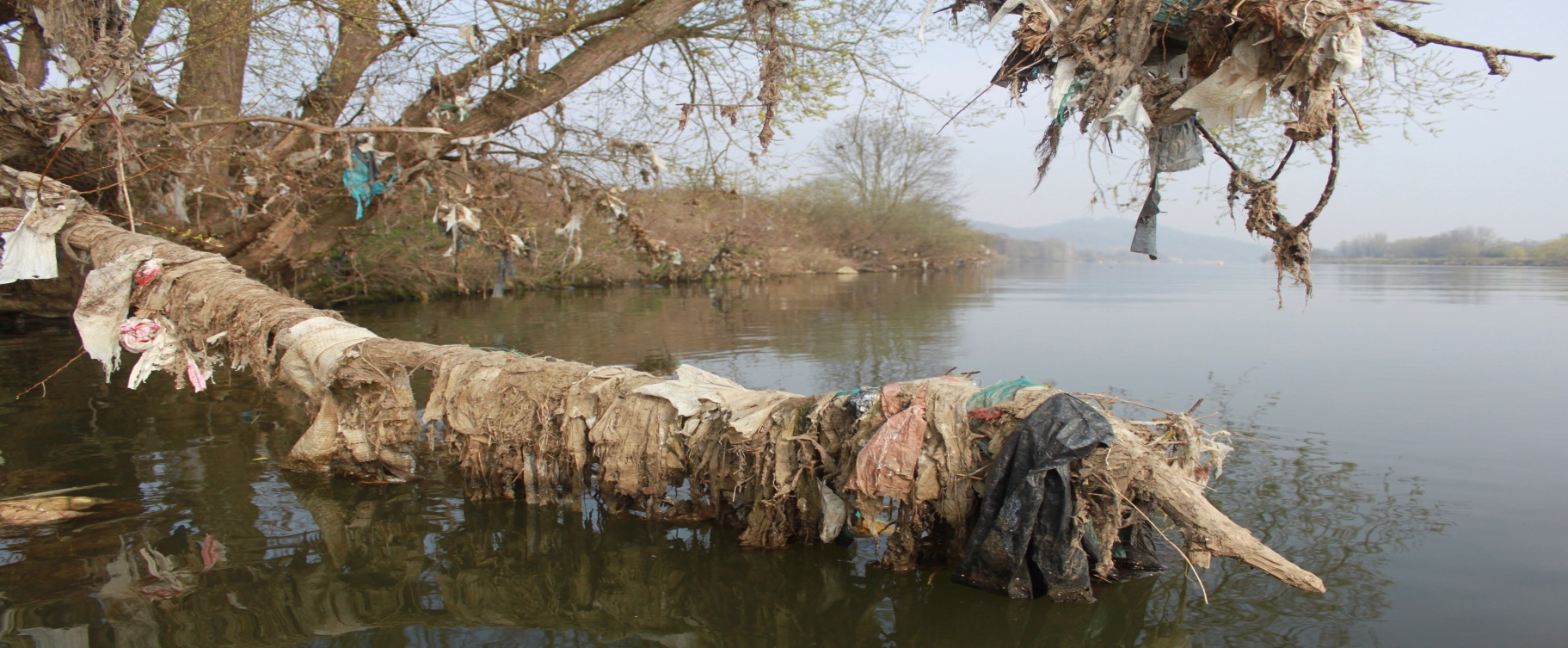
Riverine litter input is estimated to be a major contributor to marine litter, but there is no comprehensive information about the amount of litter being transported through rivers to the sea. Furthermore, there are no harmonised methodologies for providing quantitative data for comparable assessments of riverine litter. |
This technical report compiles the options for monitoring riverine litter and quantifying litter fluxes, focusing on anthropogenic litter. It includes the current scientific and technical background regarding litter in river systems, their flow regime and basic properties. The document aims to provide recommendations for monitoring approaches and methodologies. It also provides indications on the issues which need to be further developed in a collaborative approach. |
An extensive literature review has been performed in order to identify the existing options for the monitoring of litter items in rivers. Different monitoring methods are used in two environmental compartments: river water bodies and riverbanks. For a river water body, the river water surface can be monitored by visual observation and image acquisition, while collection methodologies for the water column include the use of retaining structures and sampling using grids, nets and filtration systems (with different mesh sizes and openings) at different water depths. Riverbank monitoring comprises the observation and eventual collection of litter items and sediment samples from the riverbanks. Methodologies are described and technical details are reported whenever available. |  |
Rivers with a watershed population > 1 million inhabitants. |
As methodologies are further developed and basic research is ongoing, only some initial recommendations can be made. General recommendations highlight the need for additional scientific knowledge, which should be made accessible to facilitate communication and coordination among key players in order to harmonise efforts and provide guidance at international level in a collaborative way. Knowledge gaps should be filled by analysing the outcome of these ongoing activities (the recommendations include a list of identified gaps). As there are no agreed monitoring methodologies at the international level, guidance on the monitoring of riverine litter is needed, including metadata requirements and reporting units. In order to quantify riverine litter input to the marine environment, monitoring methods have to provide data that can be related to river flow in order to be able to calculate litter fluxes (e.g. visual observation of the river water surface and collection method for the river water body). The JRC RIMMEL project has provided a a network and tools for use in riverine litter monitoring. |
